创建zfs 池 zfs_raid0为名称池名称,可以修改
zpool create zfs_raid0 /dev/sda /dev/sdb
查看zfs池是不是生效
zpool status zfs_raid0
创建挂载点
mkdir -p /mnt/zfs_raid0
挂载zfs池到挂载点
zfs set mountpoint=/mnt/zfs_raid0 zfs_raid0
PVE中挂载
选择此项
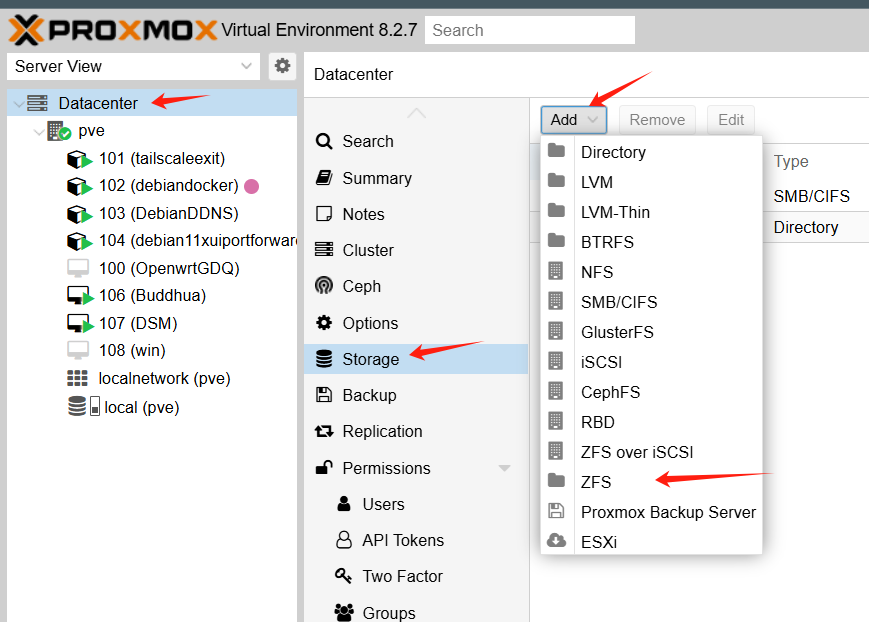
填入
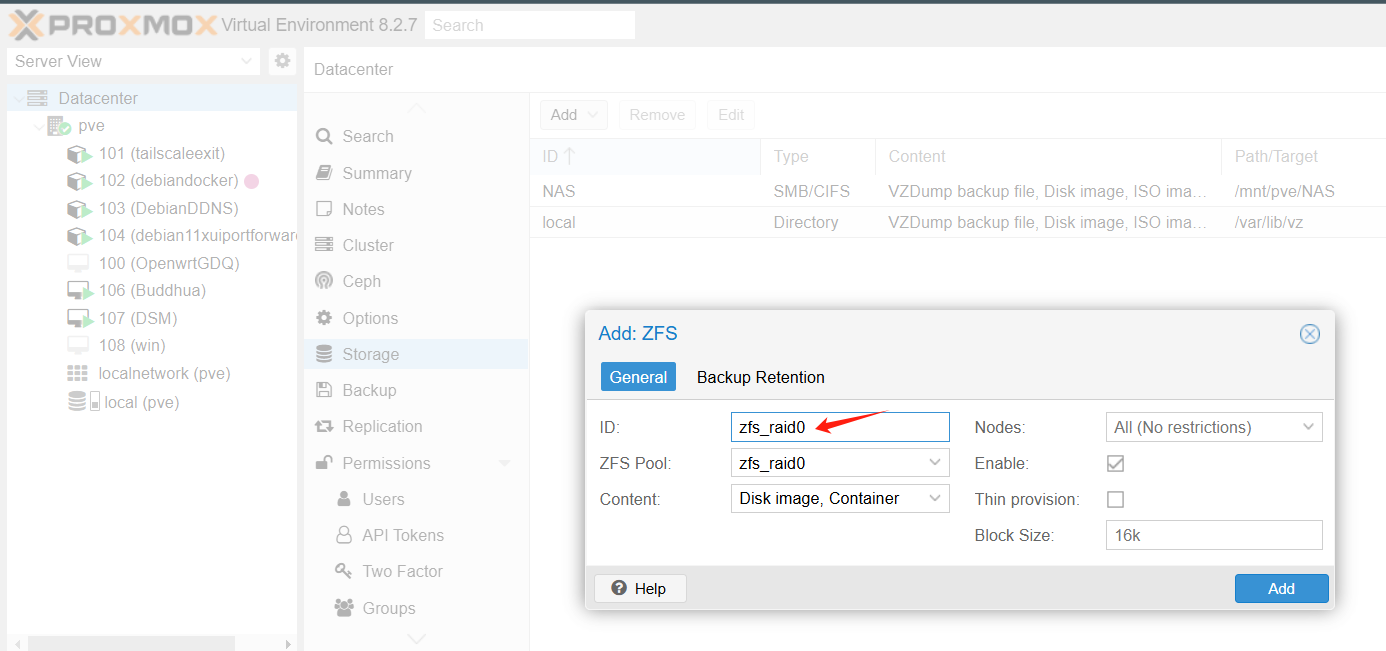
添加成功
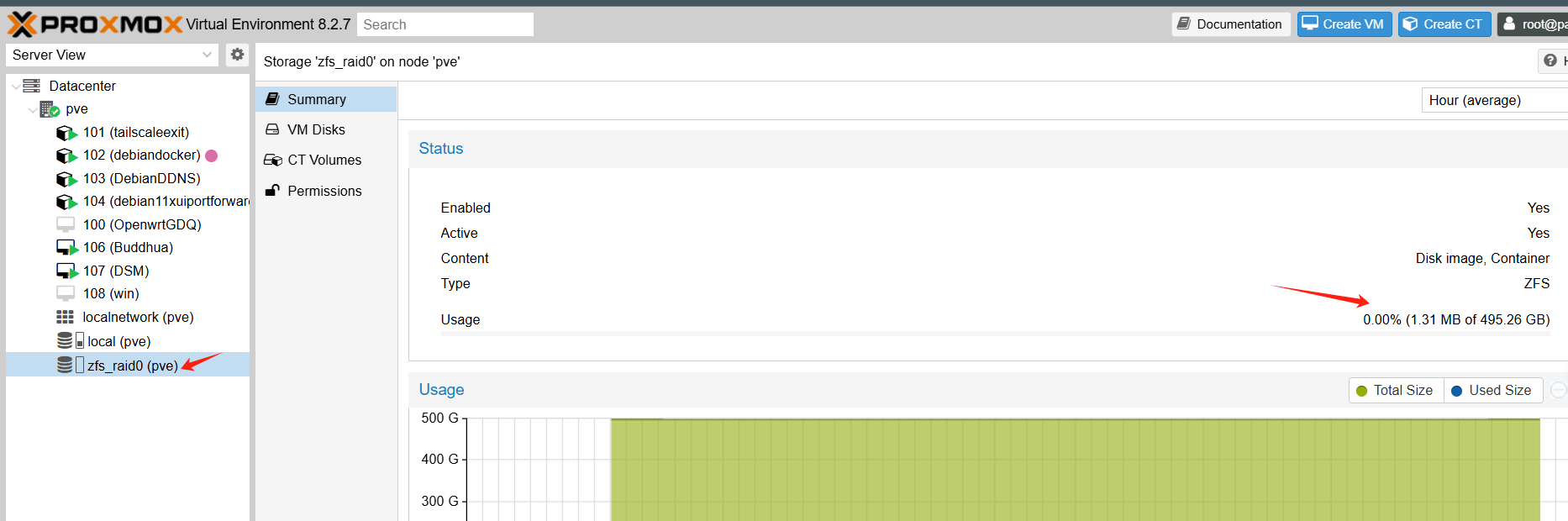
查看是否挂载成功
df -Th
Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
zfs_raid0 zfs 462G 128K 462G 1% /mnt/zfs_raid0
修改ARC ram 缓存大小 nano /etc/modprobe.d/zfs.conf
添加以下
options zfs zfs_arc_max=1073741824 #单位为bytes,此设置为最大1G
options zfs zfs_arc_min=536,870,912 #最小500MB
更新系统
update-initramfs -u -k all
重启
reboot
重启后检查
cat /sys/module/zfs/parameters/zfs_arc_min
cat /sys/module/zfs/parameters/zfs_arc_max
arcstat
arc_summary | more
arc_summary -d | more
测速
写1G
dd if=/dev/zero of=/mnt/zfs_raid0/testfile bs=1G count=1 oflag=direct
读1G
dd if=/mnt/zfs_raid0/testfile of=/dev/null bs=1G count=1 iflag=direct
zfs格式化的硬盘重装系统需要先把zfs标签删除才可以重装系统
zpool labelclear -f /dev/sdX
zpool destroy poolname
wipefs -a /dev/sdX
非zfs可以一次删除多个盘属性,如ext4, btrfs等,但是zfs需要一个个删
wipefs -a /dev/sda /dev/sdb /dev/sdc
一键自动删除zfs脚本
for d in $(zpool status -P poolname | awk '/\/dev\//{print $1}' | sort -u); do zpool labelclear -f "$d"; done
如果知道盘符路径脚本
for d in /dev/sdX /dev/sdY /dev/sdZ; do zpool labelclear -f "$d"; done
优化
nano /etc/modprobe.d/zfs.conf
options zfs zfs_arc_max=2147483648
options zfs zfs_dirty_data_max_max=4294967296
options zfs zfs_vdev_async_write_max_active=32
options zfs zfs_vdev_sync_write_max_active=16
options zfs zfs_dmu_offset_next_sync=0
应用并重启
update-initramfs -u && reboot
zpool set autotrim=on rpool
zfs set compression=lz4 rpool
zfs set atime=off rpool
zfs set sync=standard rpool
rpool为zfs默认安装名称,需要修改为实际阵列名称如zfs_raid0
zfs create rpool/llm-models #创建针对AI大模型zfs数据集,存储文件为大尺寸文件
zfs set recordsize=1M rpool/models #设置大模型zfs数据集缓存1M为大文件优化
zfs create rpool/docker-data #创建针对docker zfs数据集,存储文件为小尺寸文件
zfs set recordsize=16k rpool/docker-data
- 创建并批量设置不同的zfs数据集
zfs create rpool/data/db -o recordsize=16k
zfs create rpool/data/general -o recordsize=128k
zfs create rpool/data/media -o recordsize=1M
zfs create rpool/data/llm_models -o recordsize=1M
- zfs储存池命令
zfs list -r rpool #列出存储池中的数据集
zfs list -o name,recordsize #列出存储池中的数据集规格
zfs destroy rpool/models #销毁存储池中的数据集
优化说明
- Kernel Module Parameters in /etc/modprobe.d/zfs.conf
These are loaded before ZFS starts.
| Parameter | Purpose | Effect | My Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
zfs_arc_max=2147483648 |
Sets max ARC (RAM cache) size to 2 GB. | Limits RAM usage for ZFS cache. | Be careful — in PVE, ARC is crucial for performance, especially read-heavy loads. If you have >8 GB RAM, 2 GB may be too small and will reduce performance. I’d only set this low if you are short on RAM or running memory-heavy VMs. |
zfs_dirty_data_max_max=4294967296 |
Max dirty data (unwritten data in memory). | Bigger = more write buffering. | Can speed up sequential writes, but increases data loss risk if power fails (unless you have UPS). 4 GB is reasonable for SSDs. |
zfs_vdev_async_write_max_active=32 |
Max active async write I/O per vdev. | Higher can improve SSD/HDD write throughput. | On SSDs, 32 is fine; for HDD pools, too high can increase seek latency. |
zfs_vdev_sync_write_max_active=16 |
Max active sync write I/O per vdev. | Affects sync=always writes. |
Could help in NFS/iSCSI workloads; otherwise won’t change much. |
zfs_dmu_offset_next_sync=0 |
Changes how ZFS calculates next sync offset. | Rare tweak, usually left default. | This is an old tuning — in modern OpenZFS, gains are minimal. I’d skip it unless you know why it’s needed. |
- ZFS Pool/Dataset Settings
These are applied after pool creation.
| Command | Purpose | Comment |
|---|---|---|
zpool set autotrim=on rpool |
Enables TRIM for SSDs. | Good for SSD pools. For HDD-only pools, this does nothing. |
zfs set compression=lz4 rpool |
Enables lightweight compression. | Recommended — often improves speed by reducing I/O size. |
zfs set atime=off rpool |
Disables access time updates. | Good for performance unless you need last-access times for files. |
zfs set recordsize=16K rpool |
Changes block size for files. | Caution — ideal recordsize depends on workload. 16K is good for databases/VM disks, but bad for large media files (hurts sequential throughput). Default 128K is better for big files. |
zfs set sync=standard rpool |
Sync write behavior. | Standard = safe. Setting sync=disabled boosts speed but risks data loss on crash — fine for scratch data, not for critical VMs. |
pool-level, dataset/VM-level, and system-level optimizations:
- Pool-Level Optimizations
These affect the entire pool.
| Action | Why | Command |
|---|---|---|
Enable ashift=12 or higher when creating pool |
Ensures writes align with SSD/NVMe sector size (4K). Avoids read-modify-write penalties. | Only set at pool creation: zpool create -o ashift=12 |
Enable autotrim=on |
Keeps SSD/NVMe performance stable over time. | zpool set autotrim=on rpool |
| Compression=lz4 | Often improves speed on fast CPUs because less data is written. | zfs set compression=lz4 rpool |
| Disable unused features | Example: dedup — uses huge RAM, usually slows down. | Make sure dedup=off |
- Dataset/VM-Specific Tweaks
Instead of changing defaults for everything, tune based on usage.
| Workload | Setting | Command |
|---|---|---|
| VM disk images | Small blocks reduce wasted I/O | zfs set recordsize=16K rpool/vm-disks |
| Large media/archive files | Large blocks = fewer IOPS needed | zfs set recordsize=128K rpool/media |
| Databases / sync-heavy writes | Consider logbias=throughput |
zfs set logbias=throughput rpool/db |
| Non-critical scratch data | Can disable sync for huge speed boost | zfs set sync=disabled rpool/temp |
- System-Level / ZFS Module Tunings
These are safe for NVMe + 16 GB RAM.
/etc/modprobe.d/zfs.conf
options zfs zfs_arc_max=8589934592 # 8 GB
- Use half your RAM for ARC
options zfs zfs_dirty_data_max_max=4294967296 # 4 GB
- Allow larger write buffer
options zfs zfs_vdev_async_write_max_active=32
options zfs zfs_vdev_sync_write_max_active=16
- Boost I/O parallelism for NVMe
Then:
update-initramfs -u && reboot



评论区