Summary of Permissions
| File/Directory | Owner | Permissions | Command |
|---|---|---|---|
/home/ABC |
ABC |
755 |
sudo chown ABC:ABC /home/ABC |
sudo chmod 755 /home/ABC |
|||
/home/ABC/.ssh |
ABC |
700 |
sudo chown ABC:ABC /home/ABC/.ssh |
sudo chmod 700 /home/ABC/.ssh |
|||
/home/ABC/.ssh/authorized_keys |
ABC |
600 |
sudo chown ABC:ABC /home/ABC/.ssh/authorized_keys |
sudo chmod 600 /home/ABC/.ssh/authorized_keys |
Explanation of Permissions
-
755for/home/ABC:- The home directory should allow the owner (
ABC) full access (rwx) and others to list the directory contents (r-x). - Command:
sudo chown ABC:ABC /home/ABC sudo chmod 755 /home/ABC
- The home directory should allow the owner (
-
700for/home/ABC/.ssh:- The
.sshdirectory should allow only the owner (ABC) full access (rwx). - Command:
sudo chown ABC:ABC /home/ABC/.ssh sudo chmod 700 /home/ABC/.ssh
- The
-
600for/home/ABC/.ssh/authorized_keys:- The
authorized_keysfile should allow only the owner (ABC) to read and write (rw-). - Command:
sudo chown ABC:ABC /home/ABC/.ssh/authorized_keys sudo chmod 600 /home/ABC/.ssh/authorized_keys
- The
Why These Permissions?
-
Home Directory (
755):- Allows the owner full access while allowing others to list the directory contents (but not modify them).
-
.ssh Directory (
700):- Restricts access to the owner only, ensuring no other users can view or modify the SSH keys.
-
authorized_keys File (
600):- Ensures only the owner can read or modify the file, preventing unauthorized access.
batch script for ssh setup
#!/bin/bash
# Log file setup
log_file="/var/log/ssh_setup.log"
exec &> >(tee -a "$log_file")
echo -e "\n\033[1;34m=== SSH User and Key Setup Tool ===\033[0m"
echo "Log file created at $log_file"
# Function to check disk space
check_disk_space() {
local required_space=1048576 # 1GB in KB
local available_space=$(df / | tail -n 1 | awk '{print $4}')
if [ "$available_space" -lt "$required_space" ]; then
echo -e "\033[1;31mError: Not enough disk space available. At least 1GB is required.\033[0m"
exit 1
fi
echo -e "\033[1;32mDisk space check passed.\033[0m"
}
# Function to install sudo if it's not already installed
install_sudo() {
if ! command -v sudo &>/dev/null; then
echo -e "\033[1;33m'sudo' is not installed. Installing sudo...\033[0m"
apt update && apt install -y sudo || { echo "Failed to install sudo"; exit 1; }
echo -e "\033[1;32m'sudo' installed successfully.\033[0m"
else
echo -e "\033[1;32m'sudo' is already installed.\033[0m"
fi
}
# Function to check if SSH is installed
check_ssh_installed() {
if ! command -v sshd &>/dev/null; then
echo -e "\033[1;33m'OpenSSH Server' is not installed. Installing...\033[0m"
apt update && apt install -y openssh-server || { echo "Failed to install SSH server"; exit 1; }
echo -e "\033[1;32m'OpenSSH Server' installed successfully.\033[0m"
else
echo -e "\033[1;32m'OpenSSH Server' is already installed.\033[0m"
fi
}
# Function to set up SSH directory structure and permissions
setup_ssh_permissions() {
local username=$1
local home_dir="/home/$username"
local ssh_dir="$home_dir/.ssh"
local auth_keys="$ssh_dir/authorized_keys"
# Create .ssh directory if it doesn't exist
mkdir -p "$ssh_dir" || { echo "Failed to create .ssh directory"; exit 1; }
# Create authorized_keys file if it doesn't exist
touch "$auth_keys" || { echo "Failed to create authorized_keys"; exit 1; }
# Set ownership recursively
chown -R "$username:$username" "$ssh_dir" || { echo "Failed to set ownership"; exit 1; }
# Set directory permissions
chmod 755 "$home_dir" || echo "Warning: Failed to set home directory permissions"
chmod 700 "$ssh_dir" || { echo "Failed to set .ssh permissions"; exit 1; }
chmod 600 "$auth_keys" || { echo "Failed to set authorized_keys permissions"; exit 1; }
echo -e "\n\033[1;32mSetup completed for user: $username\033[0m"
echo -e "Directory: $ssh_dir"
echo -e "Permissions:"
echo -e " - .ssh: $(stat -c %A "$ssh_dir")"
echo -e " - authorized_keys: $(stat -c %A "$auth_keys")\n"
}
# Function to generate SSH key pair
generate_ssh_key() {
local username=$1
local ssh_dir="/home/$username/.ssh"
# Check if an SSH key already exists
if [ -f "$ssh_dir/id_rsa" ]; then
read -p "An SSH key already exists for this user. Do you want to overwrite it? (y/n): " overwrite_key
if [[ "$overwrite_key" =~ [Nn] ]]; then
echo -e "\033[1;33mUsing existing SSH key for the user.\033[0m"
return # Exit the function without generating a new key
fi
fi
# Ask if the user wants to use a passphrase
read -p "Do you want to use a passphrase for the SSH key? (y/n): " use_passphrase
if [[ "$use_passphrase" =~ [Yy] ]]; then
# Generate SSH key pair with a passphrase
echo -e "\033[1;33mGenerating SSH key pair with a passphrase for user '$username'...\033[0m"
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -f "$ssh_dir/id_rsa" -C "$username@$(hostname)"
else
# Generate SSH key pair without a passphrase
echo -e "\033[1;33mGenerating SSH key pair without a passphrase for user '$username'...\033[0m"
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -f "$ssh_dir/id_rsa" -N "" -C "$username@$(hostname)"
fi
# Set ownership and permissions for the keys
chown "$username:$username" "$ssh_dir/id_rsa" "$ssh_dir/id_rsa.pub"
chmod 600 "$ssh_dir/id_rsa"
chmod 644 "$ssh_dir/id_rsa.pub"
echo -e "\033[1;32mSSH key pair generated successfully.\033[0m"
}
# Function to test SSH key authentication
test_ssh_key_auth() {
local username=$1
local ssh_dir="/home/$username/.ssh"
echo -e "\033[1;33mTesting SSH key authentication for user '$username'...\033[0m"
# Automatically add localhost's host key to known_hosts
ssh-keyscan -H localhost >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts
# Debugging: Show the SSH command being run
echo -e "\033[1;33mRunning: ssh -i $ssh_dir/id_rsa -o PasswordAuthentication=no $username@localhost\033[0m"
# Specify the private key explicitly
if ssh -i "$ssh_dir/id_rsa" -o PasswordAuthentication=no "$username@localhost" true; then
echo -e "\033[1;32mSSH key authentication successful for user '$username'.\033[0m"
else
echo -e "\033[1;31mError: SSH key authentication failed for user '$username'.\033[0m"
exit 1
fi
}
# Function to configure SSH security settings
configure_ssh_security() {
local sshd_config="/etc/ssh/sshd_config"
local sshd_backup="/root/backup_ssh/sshd_config.backup"
local backup_dir="/root/backup_ssh"
# Create backup directory
mkdir -p "$backup_dir" || { echo "Failed to create backup directory"; exit 1; }
# Backup the current SSH configuration
cp "$sshd_config" "$sshd_backup" || { echo "Failed to backup SSH configuration"; exit 1; }
echo -e "\033[1;32mBackup of SSH configuration created: $sshd_backup\033[0m"
# Ask if SSH port should be changed
read -p "Do you want to change the default SSH port (22)? (y/n): " change_ssh_port
if [[ "$change_ssh_port" =~ [Yy] ]]; then
read -p "Enter the new SSH port (e.g., 2222): " new_ssh_port
if [[ "$new_ssh_port" =~ ^[0-9]+$ ]] && [ "$new_ssh_port" -ge 1024 ] && [ "$new_ssh_port" -le 65535 ]; then
# Update the SSH port in the configuration file
sed -i "s/^#\?Port .*/Port $new_ssh_port/" "$sshd_config" || { echo "Failed to update SSH port"; exit 1; }
echo -e "\033[1;32mSSH port updated to $new_ssh_port.\033[0m"
else
echo -e "\033[1;31mError: Invalid port number. Port must be between 1024 and 65535.\033[0m"
exit 1
fi
fi
# Ask if root login should be disabled
read -p "Do you want to disable root login via SSH? (y/n): " disable_root_login
if [[ "$disable_root_login" =~ [Yy] ]]; then
sed -i 's/^#\?PermitRootLogin.*/PermitRootLogin no/' "$sshd_config" || { echo "Failed to disable root login"; exit 1; }
echo -e "\033[1;32mRoot login via SSH disabled.\033[0m"
fi
# Ask if password authentication should be disabled
read -p "Do you want to disable password authentication for SSH? (y/n): " disable_password_auth
if [[ "$disable_password_auth" =~ [Yy] ]]; then
sed -i 's/^#\?PasswordAuthentication.*/PasswordAuthentication no/' "$sshd_config" || { echo "Failed to disable password authentication"; exit 1; }
echo -e "\033[1;32mPassword authentication for SSH disabled.\033[0m"
fi
# Restart SSH service to apply changes
systemctl restart ssh || { echo "Failed to restart SSH service"; exit 1; }
echo -e "\033[1;32mSSH service restarted successfully.\033[0m"
}
# Function to create a backup user
create_backup_user() {
local backup_user="backupuser"
echo -e "\033[1;33mCreating a backup user with sudo privileges...\033[0m"
adduser --disabled-password --gecos "" "$backup_user" || { echo "Failed to create backup user"; exit 1; }
usermod -aG sudo "$backup_user" || { echo "Failed to add backup user to sudo group"; exit 1; }
echo -e "\033[1;32mBackup user '$backup_user' created with sudo privileges.\033[0m"
}
# Main script
clear
echo -e "\n\033[1;34mSSH User and Key Setup Tool\033[0m"
# Check if the script is run as root
if [ "$EUID" -ne 0 ]; then
echo -e "\033[1;31mError: Please run this script as root.\033[0m"
exit 1
fi
# Check disk space
check_disk_space
# Install sudo if it's not already installed
install_sudo
# Check if SSH is installed
check_ssh_installed
# Prompt for username
read -p "Enter username: " username
# Validate username
if ! [[ "$username" =~ ^[a-z_][a-z0-9_-]*$ ]]; then
echo -e "\033[1;31mError: Invalid username '$username'. Usernames must start with a letter or underscore and contain only letters, numbers, hyphens, or underscores.\033[0m"
exit 1
fi
# Check if user exists
if id "$username" &>/dev/null; then
echo -e "\033[1;31mError: User '$username' already exists. Please choose a different username.\033[0m"
exit 1
fi
# Create the user
echo -e "\033[1;33mUser '$username' does not exist. Creating user...\033[0m"
adduser --disabled-password --gecos "" "$username" || { echo "Failed to create user"; exit 1; }
echo -e "\033[1;32mUser '$username' created successfully.\033[0m"
# Set a password for the user
echo -e "\033[1;33mSetting a password for user '$username'...\033[0m"
passwd "$username"
# Ask if the user should be granted root privileges
read -p "Grant root privileges to '$username'? (y/n): " grant_root
if [[ "$grant_root" =~ [Yy] ]]; then
usermod -aG sudo "$username" || { echo "Failed to add user to sudo group"; exit 1; }
echo -e "\033[1;32mUser '$username' added to the sudo group (root privileges granted).\033[0m"
fi
# Run setup
setup_ssh_permissions "$username"
# Generate SSH key pair
generate_ssh_key "$username"
# Inject the public key into authorized_keys
echo -e "\033[1;32mInjecting SSH key for user '$username'...\033[0m"
cat "/home/$username/.ssh/id_rsa.pub" | tee -a "/home/$username/.ssh/authorized_keys" > /dev/null
# Verify the key was added
if grep -q "$(cat "/home/$username/.ssh/id_rsa.pub")" "/home/$username/.ssh/authorized_keys"; then
echo -e "\033[1;32mSSH key successfully injected for user '$username'.\033[0m"
else
echo -e "\033[1;31mError: Failed to inject SSH key for user '$username'.\033[0m"
exit 1
fi
# Test SSH key authentication
test_ssh_key_auth "$username"
# Create a backup user
create_backup_user
# Configure SSH security settings
configure_ssh_security
# Final message
echo -e "\n\033[1;35mSSH user and key setup completed for user '$username'.\033[0m"
echo -e "\033[1;33mConsider setting up periodic checks of your SSH setup and security configurations.\033[0m"
Warming: after setup complete, Do Not close the terminal before the private key downloaded to local, otherwise you will be locked out of remote access
/home/user/.ssh/id_rsa
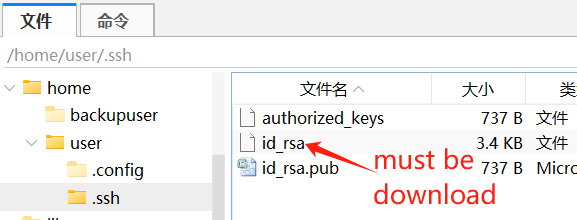
All actions will be logged to /var/log/ssh_setup.log like example in following
=== SSH User and Key Setup Tool ===
Log file created at /var/log/ssh_setup.log
SSH User and Key Setup Tool
Disk space check passed.
'sudo' is not installed. Installing sudo...
WARNING: apt does not have a stable CLI interface. Use with caution in scripts.
Hit:1 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/debian bookworm InRelease
Reading package lists...
Building dependency tree...
Reading state information...
All packages are up to date.
WARNING: apt does not have a stable CLI interface. Use with caution in scripts.
Reading package lists...
Building dependency tree...
Reading state information...
The following NEW packages will be installed:
sudo
0 upgraded, 1 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded.
Need to get 1,889 kB of archives.
After this operation, 6,199 kB of additional disk space will be used.
Get:1 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/debian bookworm/main amd64 sudo amd64 1.9.13p3-1+deb12u1 [1,889 kB]
Fetched 1,889 kB in 0s (4,859 kB/s)
Selecting previously unselected package sudo.
(Reading database ... 19775 files and directories currently installed.)
Preparing to unpack .../sudo_1.9.13p3-1+deb12u1_amd64.deb ...
Unpacking sudo (1.9.13p3-1+deb12u1) ...
Setting up sudo (1.9.13p3-1+deb12u1) ...
Processing triggers for libc-bin (2.36-9+deb12u9) ...
'sudo' installed successfully.
'OpenSSH Server' is already installed.
Enter username: User 'user' does not exist. Creating user...
Adding user `user' ...
Adding new group `user' (1000) ...
Adding new user `user' (1000) with group `user (1000)' ...
Creating home directory `/home/user' ...
Copying files from `/etc/skel' ...
Adding new user `user' to supplemental / extra groups `users' ...
Adding user `user' to group `users' ...
User 'user' created successfully.
Setting a password for user 'user'...
New password:
Retype new password:
passwd: password updated successfully
Grant root privileges to 'user'? (y/n): User 'user' added to the sudo group (root privileges granted).
Setup completed for user: user
Directory: /home/user/.ssh
Permissions:
- .ssh: drwx------
- authorized_keys: -rw-------
Do you want to use a passphrase for the SSH key? (y/n): Generating SSH key pair with a passphrase for user 'user'...
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Your identification has been saved in /home/user/.ssh/id_rsa
Your public key has been saved in /home/user/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:On/7gnoEPJXju+NbRYmmi9xyTntjZPHZt7b/ducmVGA user@debian
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 4096]----+
| . |
| + . .E |
| . o .o o. . |
| + .o.. .|
| oS. o.o . |
| . +o.o.o o .|
| *.==. . ..|
| B=o* .o=|
| .+**.=. .*X|
+----[SHA256]-----+
SSH key pair generated successfully.
Injecting SSH key for user 'user'...
SSH key successfully injected for user 'user'.
Testing SSH key authentication for user 'user'...
# localhost:22 SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_9.2p1 Debian-2+deb12u4
# localhost:22 SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_9.2p1 Debian-2+deb12u4
# localhost:22 SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_9.2p1 Debian-2+deb12u4
# localhost:22 SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_9.2p1 Debian-2+deb12u4
# localhost:22 SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_9.2p1 Debian-2+deb12u4
Running: ssh -i /home/user/.ssh/id_rsa -o PasswordAuthentication=no user@localhost
SSH key authentication successful for user 'user'.
Creating a backup user with sudo privileges...
Adding user `backupuser' ...
Adding new group `backupuser' (1001) ...
Adding new user `backupuser' (1001) with group `backupuser (1001)' ...
Creating home directory `/home/backupuser' ...
Copying files from `/etc/skel' ...
Adding new user `backupuser' to supplemental / extra groups `users' ...
Adding user `backupuser' to group `users' ...
Backup user 'backupuser' created with sudo privileges.
Backup of SSH configuration created: /root/backup_ssh/sshd_config.backup
Do you want to change the default SSH port (22)? (y/n): Enter the new SSH port (e.g., 2222): SSH port updated to 2222.
Do you want to disable root login via SSH? (y/n): Root login via SSH disabled.
Do you want to disable password authentication for SSH? (y/n): Password authentication for SSH disabled.
SSH service restarted successfully.
SSH user and key setup completed for user 'user'.
Consider setting up periodic checks of your SSH setup and security configurations.



评论区